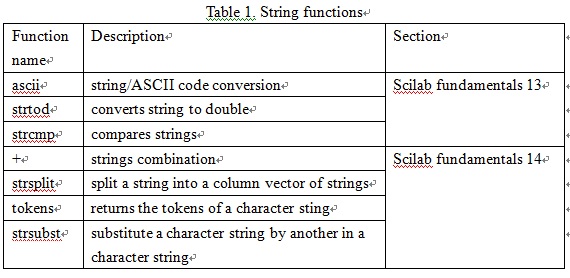
The symbolic functions listed in Table 1 provide
the capability of processing symbols and return the calculation results in the
form of symbols. With symbolic functions, we can handle and describe arithmetic
by symbols in Scilab environment. In other worlds, we can process strings
mathematically instead of numbers.
2012年11月9日 星期五
Scilab fundamentals 14 - Strings part 2
Scilab is capable of processing strings such as
combination, conversion, and separation. These functions listed in Table 1 that are useful in programming. The functions including ascii, strtod, and strcmp, were introduced in the previous section. This asection addresses on the rest functions.
Scilab fundamentals 13 - Strings part 1
Scilab is capable of processing strings such as
combination, conversion, and separation. The following two sections will
introduce several functions listed in Table 1 that are useful in programming.
Scilab fundamentals 11 - The select statement
I have a dream (but I’m not Obama). Someday, a
beauty asks me: coffee, tea, or me? When this dream comes true, I have three
choices, and I know how to select the best one. Now we learn how to program my
dream by the select statement.
In the above example, the
variable n is defined as my selection. Consequently, the select statement
responses the answer with respect to the value of n.
Scilab fundamentals 10 - The for statement
The persons who prefer bodybuilding
know the meaning of repetition. For example, I do bench press for 7
repetitions. We can organize this example systematically as the following
statement.
Scilab fundamentals 9 - The while statement
The if statement was introduced in the previoussection. In this section, we’ll learn another statement, the while statement.
Let’s start from an example. While Lisa went to work, her baby cried. This
description implies that her baby had cried until Lisa came back. Combining
these two sentences, we got the following statement.
Scilab fundamentals 8 - The if statement
It supposes that most persons ever heard that–
If you really love me, you are willing to do everything for me. It’s very
romantic, if this statement holds. In other words, if the statement holds, I will
do everything for you, or I won’t do anything for you. Now, we reorganize the preceding
description as the following statement.
Scilab fundamentals 7 - Special matrix functions
Scilab fundamentals 6 - Other matrix operations
We have learned the methods to create matrices
and the elementary operations in previous two sections (Scilab fundamentals 4 and 5). The other common matrix
operations are introduced in this section.
Scilab fundamentals 5 - Elementary matrix operations
² Matrix
arithmetic: addition, subtraction, multiplication, and backslash
The common operators including +,
-, and*, applied on real numbers are also available with real matrices. The
operator, named backslash or left division, calculate the solution of A-1B
which represented as A\B. These matrix arithmetic operators are performed on matrix
to matrix operation, and the operation rules are defined by linear algebra. Therefore, the
dimensions of matrices must be the same for additions of matrices, i.e., two m×n matrices or two square matrices.
For multiplication, A is a m-by-n matrix and B is a n-by-m matrix. As for
backslash, A is a m-by-m matrix, and B is a m-by-n matrix.
訂閱:
意見 (Atom)